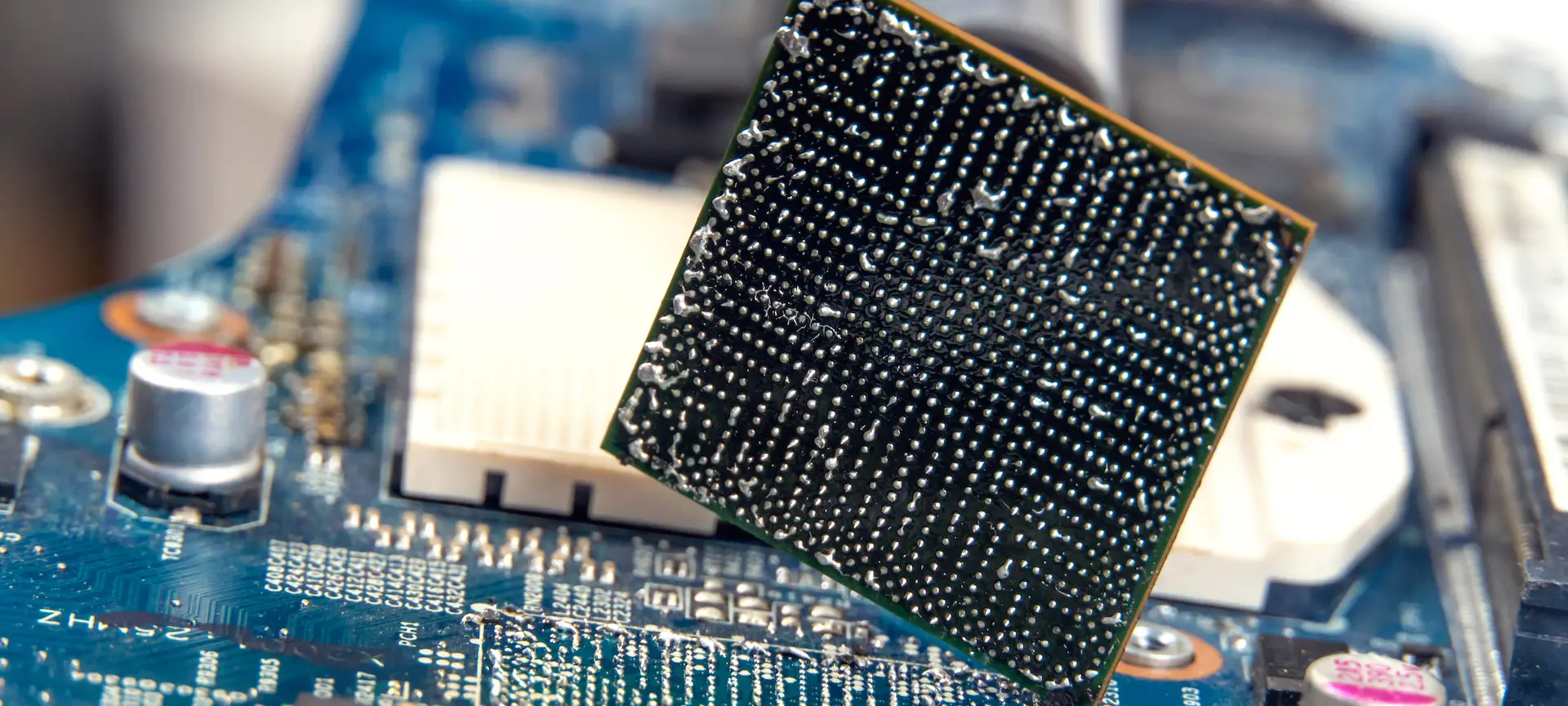
BGA Reballing Process
BGA (Ball Grid Array) reballing is a process that is becoming increasingly popular in the electronics industry. It involves removing the old solder balls from the BGA component and replacing them with new ones. This process has become a crucial step in repairing BGA components, as the failure of these components can lead to equipment malfunction and costly replacements.
In this blog, we will discuss the process of BGA reballing in detail, including its tools and materials, common mistakes, and advantages and disadvantages.
BGA Reballing
BGA components are widely used in electronic devices such as laptops, smartphones, and gaming consoles. These components have a high density of pins, usually in the form of solder balls, which allow for a reliable and compact connection to the printed circuit board (PCB). However, due to constant thermal stress and mechanical pressure, these solder balls can fail and cause the BGA component to malfunction.
This is where BGA reballing comes into play. It is an effective method of repairing BGA components that have failed due to damaged or missing solder balls. Instead of replacing the entire component, which can be costly and time-consuming, BGA reballing involves removing the faulty solder balls and replacing them with new ones.
Why is BGA Reballing Needed?
There are several reasons why BGA reballing may be necessary for electronic devices. The most common reason is a failed connection between the BGA component and the PCB due to damaged or missing solder balls. This can happen due to various factors, including thermal stress, mechanical pressure, or improper handling during manufacturing.
Another reason for BGA reballing is when the solder balls on the BGA component have experienced excessive oxidation. Oxidation can occur when the component is exposed to high temperatures or moisture, leading to the degradation of the solder balls. This can cause poor connections and eventually lead to the failure of the BGA component.
The Process of BGA Reballing
BGA (ball grid array) reballing is the process of replacing the solder balls on a BGA chip to ensure proper connections between the chip and the motherboard. This process is often necessary when a BGA chip has become damaged or when the motherboard is being upgraded.
Here are the steps involved in the BGA reballing process:
- Preparation
The first step in the BGA reballing process is to prepare the chip and motherboard. This involves cleaning both surfaces to remove any dirt, dust, or debris that could interfere with the reballing process. The chip is also inspected for any signs of damage or missing solder balls.
- Removal of old solder balls
The next step is to remove the old solder balls from the chip. This is typically done using a specialized rework station that heats the chip to a temperature high enough to melt the solder. The solder balls are then removed using a suction tool or with heat resistant gloves. Care must be taken not to damage the chip during this process.
- Cleaning the chip and applying new solder paste
Once the old solder balls have been removed, the chip is cleaned again to ensure all of the old solder and debris has been removed. Then, a new layer of solder paste is applied to the chip using a stencil. The stencil ensures that the new solder paste is applied evenly and in the correct locations.
- Placing new solder balls
After the solder paste is applied, new solder balls are placed onto the chip using a specialized tool. These balls are typically made of lead, tin, and silver alloys and come in different sizes depending on the chip being re-balled.
- Reheating the chip
Once all of the new solder balls are in place, the chip is reheated to melt the solder and allow the balls to attach to the chip. The temperature and duration of reheating depend on the type of solder being used and the size of the chip.
- Cleaning the chip again
After reheating, the chip is cleaned once again to remove any excess solder or debris. This ensures that the new solder balls are securely attached to the chip and there are no loose connections.
- Testing the chip
The final step in the BGA reballing process is to test the chip to ensure all connections are functioning properly. This is usually done using specialized equipment that checks for any shorts or open circuits.
If the testing is successful, the chip is ready to be reattached to the motherboard. If any issues are found, the reballing process may need to be repeated until all connections are working correctly.
Tools and Materials Required for BGA Reballing
- BGA Reballing Kit: This kit is specifically designed for BGA reballing and contains all the necessary tools and materials required, including a reballing stencil, reflow station, and solder balls.
- BGA Rework Station: This is a specialized heat gun that is used to reflow the solder balls onto the BGA chip. It is able to provide precise control of temperature, airflow and focus, ensuring a successful reballing process.
- BGA Reballing Stencil: This stencil is used to apply the solder balls onto the BGA chip. It comes with a specific pattern that matches the arrangement of solder balls on the chip.
- BGA Solder Balls: These are small balls of solder that are used to replace the damaged ones on the BGA chip. They come in different sizes and compositions, so it is important to select the right ones for your specific chip.
- Flux: Flux is a liquid or paste substance that is used to clean and prepare the BGA chip before reballing. It helps to remove any existing solder residue and improve the adhesion of the new solder balls.
- Kapton Tape: This is a high-temperature resistant tape that is used to hold the stencil in place on the BGA chip during the reballing process.
- Tweezers: Tweezers are important for handling the small solder balls and placing them accurately onto the BGA chip.
- Soldering Iron: A soldering iron may be needed to remove any excess solder or to touch up any areas that did not receive enough solder during the reflow process.
- Cleaning Solution: A cleaning solution is used to remove any flux residue after the reballing process is complete. This helps to prevent corrosion and damage to the chip.
- Gloves: It is important to wear gloves while handling the BGA chip and the solder balls to prevent contamination and damage. Nitrile gloves are recommended for this purpose.
- Anti-static Mat: An anti-static mat provides a safe surface to work on and prevents any static discharge that could harm the delicate components of the BGA chip.
- Microscope or Magnifying Glass: A microscope or magnifying glass is helpful for inspecting the chip and ensuring that the solder balls have been placed correctly.
- Cleaning Brushes: Small cleaning brushes can be used to remove any residual flux and debris from the BGA chip and stencil.
- Isopropyl Alcohol: This is used to clean the BGA chip and stencil after reballing. It is important to use a high-grade isopropyl alcohol (at least 90%) for best results.
- Thermal Paste: If your BGA chip requires a thermal interface material, you will need to have some thermal paste on hand to apply it before reballing.
Common Mistakes in BGA Reballing
Maintaining an immaculate layout would only get you so far in BGA rework. Itís a far too common misconception that will cost you more time and resources than necessary. While it’s important to have a meticulously laid out plan, lots of unexpected things can arise during the rework process.
Baking at the wrong temperature
This mistake is common, but luckily can be easily avoided. The reballing process requires a good amount of heat, so it’s easy to understand that the idea of increasing temperature to quicken the process is tempting. However, too much heat can lead to board and ICs damage. It’s important to follow manufacturers recommended time and temperature guidelines for baking your components.
Failing to use good quality solder paste
It’s not just the amount of heat that matters, but the quality of the soldering paste plays a key role in this process. The common formula is the leaded solder paste. Other formulas may not have the same refinements or quality control (environment/temperature). Prior to purchasing paste, make sure that it is the correct one your Process Engineer or Rework Operator recommends.
Moving components too soon
It’s tempting to remove your solder stencil and start informally cleaning after the process is complete. But it’s imperative that you wait 10 seconds after lifting your BGA heater and 45 seconds after the circuit board is removed from the bottom heat source before they are moved. If the circuit board is moved too soon, it leads to cold solder joints or a twisted ball that interferes with the reflow joint.
Poor alignment and not reflow soldering at high temperature
When poor alignment and not reflow soldering high temperature, this can result in an excess of solder paste on the ball grid array. If you aren’t reflowing it at a high enough temperature, your joints will not form as expected. Additionally, if your stencil has been used for a while, bent or warped, it may result in stencil print issue leading to poor alignment. The only way to fix this is to make sure that you use a brand new stencil in good condition.
Advantages and Disadvantages of BGA Reballing
BGA reballing is a process used to replace damaged or worn-out balls on a ball grid array (BGA) component. This is often done when the original balls have been damaged due to excessive heat or physical stress, or when the component is being reused or reworked.
The process involves removing the damaged balls and replacing them with new ones using a reballing process. While BGA reballing can be an effective solution in certain situations, it also has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the main advantages and disadvantages of BGA reballing.
Advantages of BGA Reballing:
- Cost-effective: BGA reballing can be a cost-effective solution as it is more affordable than purchasing a new component. It also requires less time and labor than replacing the entire component.
- Can extend the life of components: BGA reballing can extend the life of a BGA component, especially if the issue is related to damaged or worn-out balls. This can save both time and money in the long run.
- Allows for component reuse: BGA reballing allows for the reuse of damaged or worn-out components, which can be a significant advantage in situations where the component is no longer available or is expensive to replace.
- Precision: BGA reballing is a precise process, ensuring that the new balls are aligned accurately with the component’s pads. This improves the overall quality and reliability of the component.
- Versatility: BGA reballing can be used for a variety of BGA components, making it a versatile solution for reworking BGA components.
Disadvantages of BGA Reballing:
- Requires specialized equipment: BGA reballing requires specialized equipment, such as a reballing station and solder balls, which can be expensive to purchase and maintain.
- Skill and experience: The process of BGA reballing requires a certain level of skill and experience, making it necessary to have trained personnel or outsource the work to a professional service provider.
- Potential for damage: There is a risk of damaging the BGA component during the reballing process, especially if it is not done correctly. This can lead to additional costs and delays.
- Not suitable for all situations: BGA reballing is not suitable for all situations. In some cases, it may be more effective and efficient to replace the entire component instead of reballing it.
- Can be time-consuming: BGA reballing can be a time-consuming process, especially if there are many balls that need to be replaced. This can result in longer downtime for the affected device.
Conclusion
BGA reballing is a vital process in the field of electronics repair and manufacturing. It addresses issues related to BGA components, ensuring their proper functionality and reliability. With the ability to extend the lifespan of electronic devices, reduce electronic waste, and enhance performance, BGA reballing is a cost-effective and eco-friendly solution that plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of modern electronic systems. Understanding the process and benefits of BGA reballing is essential for technicians, engineers, and anyone involved in the world of electronics.
EMSxchange Enables you to select a Printed Circuit Board, PCB Assembly, cable & wire harness assembly, and box-build suppliers meeting your Required Electronic Manufacturing Capability, capacity, and Certification Criteria from a global Electronic contact manufacturer base.
EMSxchange takes complete responsibility and ownership for your electronic manufacturing process and all its deliverables from contract manufacturing supplier selection to manufacturing to quality inspection to shipment and delivery to your door.
EMSxchange Electronic Manufacturing Partners Profile includes:
Argus Systems (AESPL) – PCB, PCBA, Cable Assembly, Box Build, Testing.