Obsolescence Management
A series of procedures known as obsolescence management can proactively reduce hazards related to a product’s lifecycle. These hazards are related to components becoming out of stock and having an impact on the creation or upkeep of a system or product.
When manufacturing is stopped because there aren’t enough active sources for a particular component is a frequent but expensive example. Companies run the danger of production stoppages costing millions of dollars if they don’t plan ahead and have mitigation procedures in place for the impending component sourcing challenges.
- Obsolescence Management is understanding the Supply Chain, the Market situation, Availability and Customer needs.
- Space Projects are mainly immune to Obsolescence, since each Project generally speaking has a specific design and a single procurement and production phase, this results in a single custom procurement within a specific time frame.
- Some Space Projects can be susceptible to Obsolescence, these include all Space Projects where the Customer wishes to maintain a system design over a given number of productions. This is the situation in the case of a Customer Standard Equipment/System or repeated productions.
- In these cases decisions on the continued availability of the part verses the future needs of the Project have to be weighed against the risk associated with future availability, obsolescence and change notices.
- There are also risks associated with Single or Multiple Procurement which have to be weighed against continued part availability, obsolescence, cost, long term storage and relife risk.
- When considering the Single or Multiple Procurement risks, attention must also be given to.
- Continued Availability of Datasheet, Specifications, Test Capability,Records.
- Future quantity needs for example production, spares, maintenance, repairs, relife,investigation.
- Method of assuring Long Term Storage of parts, Information Records and Test Capability.
Obsolescence management enables manufacturers to :
- Consider lifecycle risks and their effects before they cause expensive production problems.
- Maintain reliable data throughout the product lifetime to support business initiatives.
You should provide the best possible answers to fundamental issues before developing an obsolescence management strategy.
Obsolescence Watch
- Once a Commercial part is selected it is important to remember that Commercial parts are not subject to any formal change or cancellation notification period.
- This means that it is up to the individual Manufacturer what level of notice is given to either current customers or the market in general.
- Therefore if a Commercial part is procured against a future need or designed into a future product it will be susceptible to change or cancellation.
- It is therefore necessary to establish an Obsolescence Watch, to identify if the product is subject to change or whether further Customer procurement is required.
- Where Customers have secured their future needs and established a Long Term Storage capability, it remains important to understand the market movement of the part, its future production, part changes or planned obsolescence are all factors which will affect even the held stock.
- Any change by the Manufacturer may be an early indication of a problem with the current stock. Customers may have to evaluate the change and determine if the change effects the stock or whether a new procurement is necessary.
- It may also be the case that last time buys may be used to top up existing stocks or protect the availability of the current part design.
- Any change to the part will invalidate the established approval program and incur additional costs.
Managing Electronic Component Obsolescence
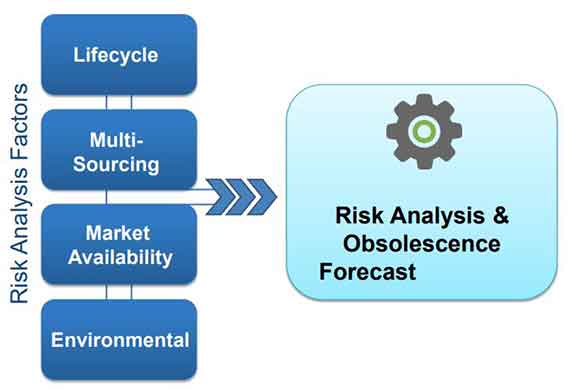
Obsolescence Management Strategies
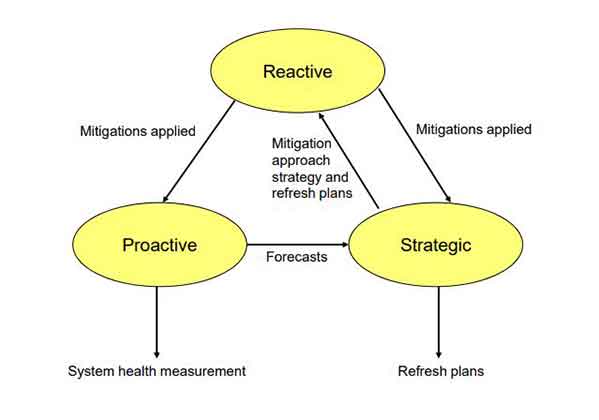
Activities in Managing Obsolescence Problem
- Forecasting – predicting obsolescence risk or dates (frequency of obsolescence)
- Mitigation – minimizing the impact of the problem after it occurs using a set of reactive firefighting approaches.
- Planning – planning design refreshes based on forecasted obsolescence dates and technology insertion roadmaps in order to minimize life cycle costs.
Part Chasing
1) Accurately provide the current status of a item, i.e., have discontinuance or last-order notices been issued?
2) Identify alternative or substitute parts.
3) Forecast the date of obsolescence.
Obsolescence Forecasting
Short-Term: Observe the supply chain for precursors to the part’s discontinuance including:
- Reduction in the number of sources.
- Reduction in inventory levels.
- Part price increases.
- Announcements made by the part manufacturer that indicate either directly or indirectly that the part is being phased out.
Long-Term: Forecasting based on part attributes and/or data mining of the historical record performed prior to the appearance of any precursors to discontinuance.
Strategy: Use long-term forecasting while continuously monitoring the supply chain for precursors. Abandon the long-term forecast when precursors appear.
Long-Term Obsolescence Forecasting Approaches
Two methods for forecasting obsolescence are used:
1) Ordinal scale approaches – weighted accumulation of “scores” assigned to a set of predetermined part type, technology and supply-chain attributes.
- Historical basis for the forecast is subjective.
- Confidence levels and uncertainties are subjective if available at all.
2) Data mining approaches – analyzing known part obsolescence dates to build vendor-specific (and vendor- independent) forecasting algorithms.
- Based on the historical record produce very accurate part-type and vendor-specific forecasts.
- Forecasts includes valid confidence levels and/or uncertainties.
EMSxchange uses a unique, proprietary vendor evaluation & qualification system to onboard vendors. We maintain a close view of their capability, capacity, and compliances. 25+ years of manufacturing experience has given us strong capabilities to understand customer requirements and supplier capabilities. EMSXchange takes complete responsibility and ownership for your electronic manufacturing process and all its deliverables from contract manufacturing supplier selection to manufacturing to quality inspection to shipment and delivery to your door. EMSxchange Electronic Manufacturing Partners Profile includes:
Argus Sytems (AESPL) – PCBA, Cable Assembly, Box Build.
Cerra Systems inc – PCB Manufacturing.




